Products
Contact us

Tel:0769-85609008
Fax:0769-85780118
E-mail:limited@shentongboli.com
Add:No.1, First Ring Road, Huaxia Industrial Zone, Langxia Village, Qiaotou Town, Dongguan City

"Hot tempered glass"
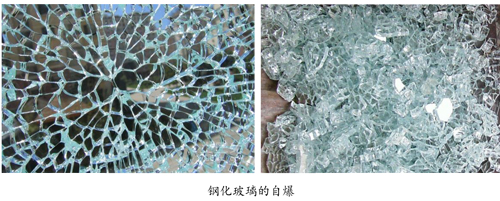
Self-explosion of tempered glass
Tempered glass has an inherent defect "self-explosion" - the phenomenon of tempered glass automatically breaking without external direct action. Tempered glass blast can occur in the process of tempering processing, storage, transportation, installation and use. There are two types of self-explosion: one is self-explosion caused by visible defects in the glass, such as stones, sand, bubbles, inclusions, notches, scratches, chipping, etc.; the second is the colorless transparent nickel sulfide in the glass ( NiS) Self-explosion caused by impurity expansion. Modern float glass production technology cannot completely eliminate the presence of nickel sulfide (NiS) impurities, so tempering and self-explosion is inevitable, which is an inherent characteristic of tempered glass. At present, there is no national standard in the world to limit the self-explosion of tempered glass. According to the experience of the Chinese glass industry, the self-explosion rate of ordinary tempered glass is about 3~5‰. The methods for solving the self-explosion of tempered glass generally include the following: 1. Reasonable design to avoid the size of the monolithic glass is too large and the structure is super thick; 2. The stress value of the tempered glass is appropriately reduced (the domestic manufacturer generally sets the surface tension of the tempered glass to 100 MPa). Left and right), use the selected tempering equipment, reasonable operation, reduce the uneven distribution of stress; 3, use excellent grade float glass or ultra-white glass, because ultra-white glass in production, a magnetic dressing process more than ordinary glass, can Further reduce the iron and nickel impurities in the raw materials. The self-explosion rate of ultra-white glass is generally only about one-tenth of a thousand; 4. The tempered glass used in important projects and important parts should be hot-dipped.
Hot dip treatment HST
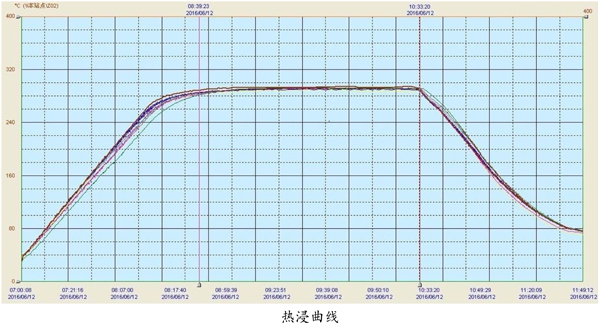
Hot dip treatment is also called homogenization treatment (known as "Heat Soak Test" in foreign countries), commonly known as "detonation". The hot dip treatment is to heat the tempered glass to 290 ° C ± 10 ° C in a "homogeneous furnace" and keep it for a certain period of time to promote the rapid completion of the phase transformation of nickel sulfide (NiS) in the tempered glass to accelerate the expansion process, so that the original use The tempered glass that may be self-explosive is artificially broken in the “homogeneous furnace” of the factory in advance, thereby reducing the self-explosion of the tempered glass in use after installation. After hot-dip tempered glass, the self-explosion rate can be reduced to about one ten-thousandth, but the hot-dip treatment does not guarantee that the tempered glass will not spontaneously explode, but only reduces the occurrence of self-explosion, and solves the troubled engineering parties. The problem of self-explosion, so hot dip is the most effective way to solve the self-explosion problem under the current technical conditions.

Hot dip standard
At present, the hot dip standard in the world mainly relies on the European standard EN14179-1:2005 for hot dip tempering glass. There are other additional standards in different regions. For example, the hot dip in Hong Kong, China requires the Hong Kong Buildings Department standard BD PNAP APP37. 1. EN14179 -1:2005: European standard/construction silicate physical tempered glass hot dip standard 2, DIN18516: German industrial standard / building peripheral tempered glass requirements and testing; 3, BD PNAP APP37: Hong Kong Buildings Department standard; GB15763.4:2009: Chinese standard "Safety glass for construction - Part 4: Homogeneous tempered glass". Hot dip test
Hot-dip tempered glass is not directly inspected at present. The method in the industry is to let manufacturers provide photos of hot dip process, hot dip curve and hot dip report or directly send people to supervise the hot dip process, as shown below: